Guide to Object-oriented Programming With Java (University at Buffalo Version)
Chapter 16: Using java.awt and javax.swing to Create GUI Applications
Up to this point, the Java programs have accepted input from and written output to the Eclipse Console window. Java provides a number or robust libraries for creating Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs). These include the java.awt.*, javax.swing.*, javafx.*, org.eclipse.swt.*, org.apache.pivot.* libraries.
Java GUI Basic Concepts
Before you can begin creating a Java GUI application you need to understand a few basic GUI concepts, such as frames, components (fields, labels, etc.), panels, layout managers, and coordinates:
- Frames
- The window (GUI) where your program’s components are held is called the Frame.
- Components
- Components consist of: text fields, radio buttons, labels, and menus. Components are all contained within the frame. Every Java application runs within a window and every window needs a frame where various components can "live".
- Panels
- The panel is the content pane is where all of your programs components are placed. You can think of the content pane as a background and the various components of your program are placed onto this background.
- Layout Managers
- The layout manager aligns components within content pane into a specific style depending on what layout you choose (BorderLayout, BoxLayout, CardLayout, FlowLayout, GridBagLayout, GridLayout, GroupLayout, SpringLayout, etc.). Certain applications are well suited for using a layout manager since they can make component placement much easier, but they can also create additional complications not typically experienced when you set your layout manager to null and assign exact coordinates for every component.
- Coordinates
- Using coordinates is important when you are not using a layout manager. Coordinates are used to specify where components are placed on the content pane. Coordinates are described just like x-y graphs from high school math class (X, Y). The (0, 0) coordinate is the top left corner of the pane. You can specify the exact position of components in your program by setting these coordinates.
Adding WindowBuilder and Swing Your Eclipse Project
Before you can run a GUI Java program you need to follow these steps to add Swing and WindowBuilder to Eclipse.
Steps to add Swing to Eclipse
- Click on:
Help - Click on:
Install New Software - In the "
Work with:" box type:neon or oxygen - From the dropdown, choose:
Neon - http://download.eclipse.org/releases/neon or /oxygen And in the second box type:Swing- Check all the boxes
- Click:
Next Click:NextAcceptthe terms- Click:
Finish - Restart Eclipse, click:
Yes
Steps to add WindowBuilder to Eclipse
- Click on:
Help - Click on:
Install New Software - In the "
Work with:" box type:neon (or oxygen) - From the dropdown, choose:
Neon - http://download.eclipse.org/releases/neon or /oxygen) - In the second box type:
window - Check all the boxes
- Click:
Next - Click:
Next Acceptthe terms- Click:
Finish - Restart Eclipse, click:
Yes
The java.awt and java.swing Libraries
To create a Java GUI application using the java.awt and java.swing libraries you first need to import the packages you need from each of them. Then you can add a layout (in this example BorderLayout) and components. Finally, you need to add the panes to the frame and make the frame using frame.setVisable(true). This creates the pop-up GUI application.
package buffalo.edu.fa23..put-your-username-here;
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import java.awt.Color;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
public class MyFirstFrame {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame frame = new JFrame(); // Create the window frame
frame.getContentPane().setBackground(Color.white);
frame.getContentPane().setForeground(Color.white);
frame.setForeground(Color.white);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(Jframe.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setTitle("My First Frame");
JPanel bluePanel = new JPanel();
JPanel redPanel = new JPanel();
JLabel label = new JLabel(" <-- pick your side --> ");
frame.getContentPane().add(label, BorderLayout.CENTER);
bluePanel.setBackground(Color.blue);
redPanel.setBackground(Color.red);
frame.getContentPane().add(bluePanel, BorderLayout.LINE_START);
frame.getContentPane().add(redPanel, BorderLayout.LINE_END);
JButton blueButton = new JButton("PICK BLUE TEAM");
JButton redButton = new JButton("PICK RED TEAM");
bluePanel.add(blueButton);
redPanel.add(redButton);
frame.pack();
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
MyFirstFrame.java Using BorderLayout Code
Here is a list of Java background and foreground colors.
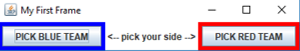
MyFirstFrame.class OutputLet's get started with a GUI program!


