Guide to Oracle SQL (Buffalo State University Version)
Maintaining a Database using SQL Statements
Oracle uses the Structured Query Language (SQL) to create and maintain the database and tables. SQL [rovides statements that allow database administrators and users to perform create, read, update, and delete (CRUD) operations on a database. SQL is broken down into four (4) areas: a data query language (DQL), a data definition language (DDL), a data control language (DCL), and a data manipulation language (DML). SQL statements are not case-sensitive. I almost always try to upper case my SQL statements just for readability. I also try to use camel-case fo my database, table, and field names. For example, employeeTable and firstName.
After you login to your bscacad3.buffalostate.edu account, type: sqlplus to enter the SQL appliaction whetre you can enter SQL statements at the SQL> prompt.
To use Oracle on your local machine, you need to download Oracle Database Express 18c page. After you install 18c, then you can download and install SQL Developer.
If you are using SQL Developer, then right-click on your connection in the SQL developer Connections window. To create a new connection, click the "plus-sign" icon in the "Oracle Connections" pane. Then, you may have to change the connect type from "Basic" to "TNS".
Then choose Open SQL Worksheet. This is where you can enter SQL statements.
The CREATE Statement
The SQL CREATE statement can be used to create a new database or a new table within an existing database if you have permissions that allow you to create a new database.
The CREATE DATABASE Statement
The SQL CREATE DATABASE databaseName statement can be used to create a new database.
CREATE DATABASE jimTest;
Database JIMTEST created.
CREATE DATABASE StatementThe CREATE TABLE Statement
The SQL CREATE TABLE tableName statement can be used to create a new table within an existing database.
CREATE TABLE jimTable ( jimID NUMBER(9), firstName VARCHAR2(25) NOT NULL, lastName VARCHAR2(25) NOT NULL, CONSTRAINT pk_jimID PRIMARY KEY (jimID) ); Table JIMTABLE created.
CREATE TABLE StatementThe DROP TABLE Statement
The SQL DROP TABLE tableName statement can be used to delete a within an existing database.
DROP TABLE jimTable
Table "JIMTABLE" dropped.
DROP TABLE StatementThe DESCRIBE Statement
In SQL Developer pressing the SHIFT-F4 key displays the table structure.
DESCRIBE jimTable; COLUMN_NAME DATA_TYPE NULLABLE DATA_DEFAULT COLUMN_ID Comments 1 JIMID NUMBER(9,0) No 1 2 FIRSTNAME VARCHAR2(25 BYTE) No 2 3 LASTNAME VARCHAR2(25 BYTE) No 3
DESCRIBE Statement Using the Run Button in SQL DEVELOPERThe INSERT Statement
The INSERT statement is used to add a record to a table. String (VARCHAR2) values should be enclosed in single quotes (''). In SQL Developer, if you are entering multiple statements you need to highlight all the statements before clicking the run icon ( ).
).
INSERT INTO jimTable (jimID, firstName, lastName) VALUES (1, 'Jim', 'Gerland'); INSERT INTO jimTable (jimID, firstName, lastName) VALUES (2, 'Phil', 'Phailure'); INSERT INTO jimTable (jimID, firstName, lastName) VALUES (3, 'Sally', 'Smart'); 1 row inserted. 1 row inserted. 1 row inserted.
INSERT StatementIn SQL Developer, click the Commit ( ) icon to apply the results of your
) icon to apply the results of your INSERT query to your database.
The SELECT Statement
The SELECT statement is used to retreive information from the database.
Using the SELECT Statement To Retreive Records
The asterisk (*) is used as a wildcard. It is used to retreive all the fields in the table.
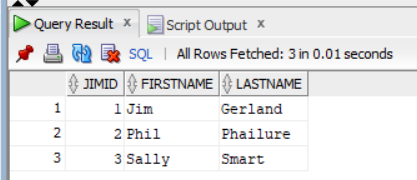
SELECT * FROM jimTable; JIMID FIRSTNAME LASTNAME 1 1 Jim Gerland 2 2 Phil Phailure 3 3 Sally Smart
SELECT All Fields StatementIf you click the run script icon ( ) in SQL developer you get a different type of output.
) in SQL developer you get a different type of output.
SELECT * FROM jimTable;
SELECT All Fields StatementUsing the SELECT Statement To Retrieve Certain Fields
You can also name the fields you would like return using the SELECT field[s] statement.
SELECT firstName, lastName FROM jimTable FIRSTNAME LASTNAME 1 Jim Gerland 2 Phil Phailure 3 Sally Smart
SELECT Certain Fields StatementThe UPDATE Statement
The UPDATE statement can be used to modify an existing record in a table.
UPDATE jimtable SET firstName = 'James' WHERE jimID = 1; 1 row updated.
UPDATE StatementThe DELETE Statement
The DELETE statement can be used to remove an existing record from a table.
DELETE FROM jimtable WHERE jimID = 1; 1 row deleted.
DELETE StatementThe TRUNCATE Statement
The TRUNCATE statement is used to remove all the records in a table but keep the strucure (fields) of the table intact.
TRUNCATE TABLE jimTable;
TABLE JIMTABLE truncated.
UPDATE StatementSQL Comments
It is important to comment your SQL code. This helps you when you need to go back and modify your code and it helps other devlopers who will need to maintain you code after you move on to new, more challenging projects. SQL provides two (2) types of comments. single line comments (--) and multiple line comments (/* */).
-- This is a single line comment /* This is a multiple line comment */ SELECT * FROM countries; COUNTRY COUNTRY_NAME REGION_ID ---------- ------------------------------ ---------- 1 Argentina 2 2 Brazil 2 3 Canada 2 4 United States 2 5 Mexico 2
Task - Create, Populate, and Display an employees Table
Requirements
- Open SQL Developer
- Connect to your database instance
- Open a new SQL editor window
- Enter code to CREATE an "employees" table with these fields:
employee_id NUMBER NOT NULL, first_name VARCHAR2(20),
last_name VARCHAR2(25), email VARCHAR2(25), phone_number VARCHAR2(20),
hire_date DATE, job_id VARCHAR2(10), salary NUMBER(8,2), commission_pct NUMBER(8,2), and
department_id NUMBER(3) with employee_id as the PRIMARY KEY - INSERT these records into the "employees" table:
- 176, Sarah, Hall, sarah.hall@oca.com, 7165551231, to_date('10-SEP-2009', 'DD-MON-YYYY'), 125000, SA_MAN, 80
- 102, Allison, Felix, Allsion.felix@oca.com, 7165551232, to_date('10-OCT-2008', 'DD-MON-YYYY'), 45000, IT_PROG, 60
- 201, LoLo, Jones, lolo.jones@oca.com, 7165551234, to_date('10-SEP-2012','DD-MON-YYYY'), 55000, MK_REP, 20
- 200, Steve, Scott, steve.scott@oca.com, 7165551235, to_date('10-MAR-2011','DD-MON-YYYY'), 55000, AD_ASST, 90
- 202, Charlie, Wertz, charlie.wertz@oca.com, 7165551236, to_date('01-SEP-1989','DD-MON-YYYY'), 555000, SA_MAN, 80
- Display the employees table date (use SELECT).
- Save your SQL query script as "create_employees.sql".
When you have this Assignment ready for me to view and grade, you should click on this assignment and then choose "Add a File" and upload your create_employees.sql file, so I can download it and grade your work.