Guide to Oracle SQL (Buffalo State University Version)
Introduction to Databases
Wikipedia defines a database as "an organized collection of data. It is the collection of schemas, tables, queries, reports, views and other objects. The data are typically organized to model aspects of reality in a way that supports processes requiring information, such as modelling the availability of rooms in hotels in a way that supports finding a hotel with vacancies."
A schema is "its structure described in a formal language supported by the database management system (DBMS). The term "schema" refers to the organization of data as a blueprint of how the database is constructed (divided into database tables in the case of relational databases).
A table is a collection of related data held in a structured format within a database. It consists of fields (columns), and rows. In relational databases and flat file databases, a table is a set of data elements (values) using a model of vertical columns (identifiable by name) and horizontal rows (a record), the cell (field) being the unit where a row and column intersect.
Name Null? Type ----------------------------------------- -------- ---------------------------- SID NOT NULL VARCHAR2(9) S_LNAME NOT NULL VARCHAR2(10) S_FNAME NOT NULL VARCHAR2(10) GENDER VARCHAR2(1) MAJOR VARCHAR2(3) GPA NUMBER(3,2) SAT NUMBER(5) DOB DATE
Data Types
Each record contains fields that hold the data for that record. A field has a data type, such as Integer (NUMBER), string (VARCHAR/LONG), date (DATE), large objects (BLOB/CLOB)).
- CHAR
- Used to store fixed length character data. For example, a state field would be CHAR(2).
- VARCHAR2
- Used to store variable length character data. For example, a firstName field would be VARCHAR2(25). This allows the field to be any number of characters between 0 and 25.
- NUMBER
- Used to store integer data. For example, the age field would be NUMBER(2).
- NUMBER can also be used to store floating point (decimal) data. For example, a currency field would be NUMBER(9,2) which allows 7 digits to the left of the decimal point and 2 digits to the right of the decdimal point.
- DATE
- Used to store the year (including the century), the month, the day, the hours, the minutes, and the seconds (after midnight).
- LOB (Large OBject)
- BLOB - Used to store unstructured binary data.
- CLOB - Used to store database character set data.
- NCLOB - Used to store Unicode national character set data.
- BFILE - used to store a pointer to a binary file in the operating system outside the database.
Normalization
Normalization is the process of structuring a relational database in accordance with a series of so-called normal forms in order to reduce data redundancy and improve data integrity..
Using SQLPlus on bsuacad.buffalostate.edu
SQLPlus is a command line interface for interacting with the BUffalo State Oracle Server. Before you can use the sqlplus command you need to add a few things to your .bashrc file on the bscacad3.buffalostate.edu server.
- Login to your
bsuacad.buffalostate.eduaccount using PuTTy using your BSC Username and Password.
Your oracle-password is a capital B plus your Student ID and if your Student ID has 7 digits then add a zero in front of your Student ID and if it has 6 digits then add two (2) zeros.
For example:
Student ID: 1234567 Oracle Password: B01234567Student ID: 987654 Oracle Password: B00987654 - Edit your
.bashrcfile using the vi editor (see the Washington University site for more information about Using VI) to setup the your Oracle environment and your sqlplus alias: - At the Unix
$prompt type:vi .bashrc - Use the arrow keys to move to this line:
fi - Use
SHIFT-Ato enterAppendmode. - Then add these lines:
ORACLE_BASE=/home/oracle/db; export ORACLE_BASE
ORACLE_HOME=/home/oracle/db/product/12.1.0/dbhome_1; export ORACLE_HOME
ORACLE_SID=acad12c; export ORACLE_SID - Press
CONTROL-]to exitAppendmode. - Use the arrow keys to move to this line:
PATH=PATH/bin: - Use
SHIFT-Ato enterAppendmode. - Add this to the end of that line:
PATH=PATH=$PATH:$ORACLE_HOME/bin: - Press
CONTROL-]to exitAppendmode. - Scroll to the end of the file
- Press
SHIFT-Ato enterAppendmode. - Press the
ENTERkey to go to the next line - Type this line:
alias sqlplus=cd public_html; sqlplus your-userid/your-Oracle-password' - Press
CONTROL-]to exit the append mode. - Press the colon (
:) key to move to thevicommand prompt. - To save your
.bashrcfile, at the (:prompt, type:wq - At the Unix
$prompt type:source .bashrc - At the Unix
$prompt type:sqlplus - At the
SQL>prompt type:DESC testTable; - There should not be any listed yet, so you should see:
SQL> desc testTable;SQL>
ERROR: ORA-04043: object testTable does not exist - To create a table, at the
SQL>prompt type:
CREATE TABLE testTable
(testId NUMBER(6) NOT NULL,
firstName varchar2(25) NOT NULL,
lastName varchar2(25) NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT id_pk PRIMARY KEY (testId)
); - At the
SQL>prompt type:DESC testTable; - You should see:
Name Null? Type ----------------------------------------- -------- ---------------------------- TESTID NOT NULL NUMBER(6) FIRSTNAME NOT NULL VARCHAR2(25) LASTNAME NOT NULL VARCHAR2(25)
- To add data to your table type:
INSERT INTO testTable (testID, firstName, lastName)
VALUES (1, 'your first name', 'your last name'); - You should see:
1 row created.
- To view the data in your table type:
SELECT * FROM testTable ORDER BY lastName, firstName; - You should see:
TESTID FIRSTNAME LASTNAME ---------- ------------------------- ------------------------- 1 Jim Gerland - To exit
sqlplus, at theSQL>prompt type:exit - You should now be back at the Unix
$prompt. - To logout type:
exit
bscacad3.buffalostate.edu Account To Use sqlplusUsing SQL Developer
SQL Developer is a graphical interface to an Oracle database. You can download SQL Developer from the Oracle download site. Installation instructions are also available on that site. You also need to download and install the Oracle Express database.
Setting Up a Connection
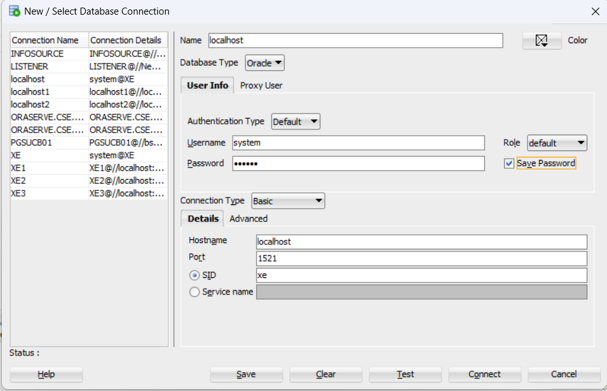
SQL Developer New Connection Window- In the Name field, type:
localhost - In the Username field, type:
system - In the Password field, type:
oracle - Check the Save Password box.
- In the Hostname field, type:
localhost - In the SID field, type:
acad12c - Click: Test
- If the test is successful then click: Connect
You should now see your connection in the right side Connections navigation window.
SQL Developer New Connection Settings

